Pre-defined elements
On this page
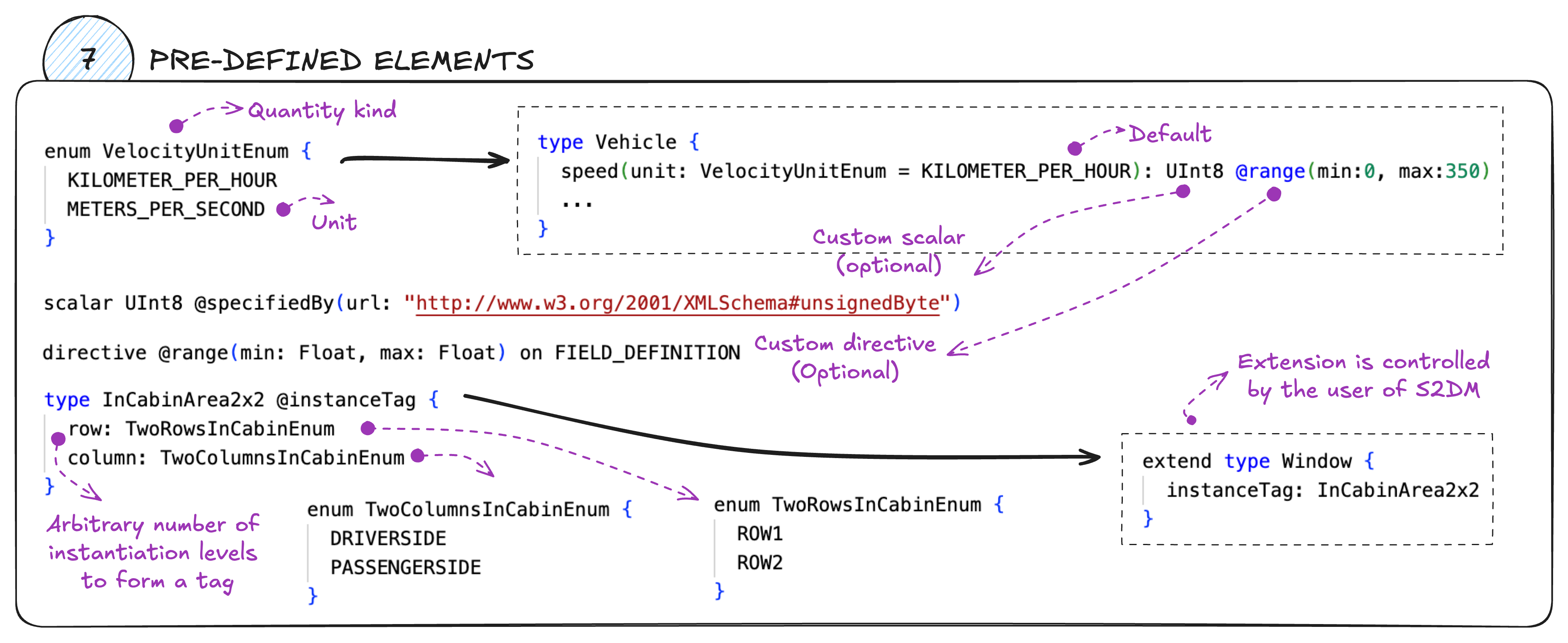
Units
Units are represented as enum values. For example:
enum VelocityUnitEnum {
KILOMETER_PER_HOUR
METERS_PER_SECOND
}The name of the enum itself refers to the quantity kind (e.g., Velocity).
A set of commonly used units is provided in the file unit_enums.graphql.
It is planned to adopt and reuse an existing standard data model for units. See issue #43 for details. Currently, the units file is inspired by the COVESA VSS Units file. The tentative model for future use is QUDT units.
Custom scalars
Scalars in GraphQL are basically the datatypes to which a field resolves.
GraphQL supports a few built-in scalars such as Int, Float, String, Boolean, and ID.
It is possible to define custom ones.
The file /spec/custom_scalars.graphql contains custom scalars that could be referenced in the model.
Custom directives
@instanceTag
directive @instanceTag on OBJECTTODO: Add description and example
@cardinality
directive @cardinality(min: Int, max: Int) on FIELD_DEFINITIONTODO: Add description and example
@range
directive @range(min: Float, max: Float) on FIELD_DEFINITIONTODO: Add description and example
@noDuplicates
directive @noDuplicates on FIELD_DEFINITIONConsidering the following generic object:
type MyObject {
field: <outputType>
}By default, the GraphQL SDL let us express the following six combinations for output types in fields:
| Case | Description | outputType |
|---|---|---|
| Nullable Singular Field | A singular element that can also be null. | NamedType |
| Non-Nullable Singular Field | A singular element that cannot be null. | NamedType! |
| Nullable List Field | An array of elements. The array itself can be null. | [NamedType] |
| Non-Nullable List Field | An array of elements. The array itself cannot be null. | [NamedType]! |
| Nullable List of Non-Nullable Elements | An array of elements. The array itself can be null but the elements cannot. | [NamedType!] |
| Non-Nullable List of Non-Nullable Elements | List and elements in the list cannot be null. | [NamedType!]! |
Implicitly, lists here refer to an array of values that could be duplicated. In order to explicitly say that the intended content of the array should function as a set of unique values instead, the custom directive @noDuplicates is introduced.
type Person {
nicknamesList: [String] # Array with possible duplicate values
nicknamesSet: [String] @noDuplicates # Set of unique values
}Common types
Common enumeration sets
In some cases, it is practical to refer to a particular set of values that might fit to multiple use cases.
For example, the zone inside the cabin of a car could be re used by the Door and the Window
It could be modeled as:
type InCabinZone {
row: InCabinRowEnum!
side: InCabinSide!
}
enum InCabinRowEnum {
FRONT
REAR
}
enum InCabinSide {
DRIVER_SIDE
PASSENGER_SIDE
}Then, it can be referenced from:
Window {
instance: InCabinZone
...
}
Door {
instance: InCabinZone
...
}Such common enumeration sets are available in the file /spec/common_enums.graphql.
Common objects of interest
Under construction…